Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of the joints. It is a term used to describe over 200 types of joint conditions. Two of the main symptoms that are associated with arthritis are pain and stiffness.
Arthritis Pain
Arthritis pain can be debilitating. In fact, the CDC reports that over one-third of adults who suffer from arthritis are limited in their activities and work.
A few of the most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and fibromyalgia. All three of these conditions cause different kinds of pain.

Pain and Stiffness Due to Arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis causes the cartilage inside the joints to disintegrate. Cartilage acts as a cushion for your bones, so when this break down occurs, the bones of your joints may rub directly against one another. This causes severe pain. However, the pain caused by osteoarthritis varies from patient to patient, depending on location and severity.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune disease. It causes the immune system to attack the body, resulting in inflammation and pain. Psoriatic arthritis can cause a variety of pain to different areas of the body. PsA affects the joints, which causes arthritis. Arthritis affects the soft tissue, tendons, and ligaments that attach to bones causing enthesitis. It can also affect the skin, which causes psoriasis.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a central pain syndrome. Central pain syndrome means your body and brain are affected by pain differently from others. A normal movement for others may cause you severe pain, or something that is painful for others may be excruciating for you. This pain can be widespread – meaning your whole body is affected. But fibromyalgia pain can come and go or be constant. It all depends on the patient.
Stiffness Caused by Arthritis
Joint stiffness is common in patients suffering from arthritis. This is because the stiffness is caused by inflammation. The inflamed area of a joint is typically worsened after periods of inactivity – especially prolonged sitting or standing. Stiffness is particularly common in the morning after a good night’s rest. However, the type of stiffness can be determined by the type of arthritis the patient has.
Rheumatic arthritis causes stiffness after a period of rest. This can occur after sitting for a long period of time, such as at a desk job or sitting in a movie theater. Standing up and walking slowly helps diffuse the stiffness.
Inflammatory arthritis causes a different kind of stiffness. This is temporary stiffness that lasts for a short amount of time. This is most common in arthritis patients in the morning, with the stiffness wearing off after approximately 30 minutes.
Get Relief from Your Pain and Stiffness
The length of time you feel joint pain and stiffness can help your physician determine the type of arthritis you have. Medication is not usually recommended, but the pain and stiffness can be reduced through the use of alternating hot and cold compresses, physical therapy, and exercise to increase your range of motion.
If you are living with arthritis and in daily pain, the team at Progressive Pain Management can help. Contact us today by filling out the form below.
Peripheral neuropathy is the term used for disorders caused by damage to the body’s peripheral nervous system.
The peripheral nervous system connects nerves from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. Including, but not limited to, the arms, legs and feet, joints, eyes, nose, and even the skin. Peripheral neuropathy is when nerves are damaged and cannot send messages from the brain to other body parts. This damage can cause numbness or pain in these affected areas.

How to Diagnose and Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can be separated into two categories: polyneuropathy and mononeuropathy. People most commonly suffer from polyneuropathy.
- Polyneuropathy is when multiple nerves are affected
- Mononeuropathy occurs when only one nerve is affected
How is Peripheral Neuropathy Diagnosed?
There are many symptoms of peripheral neuropathy, such as numbness and tingling, severe sensitivity to touch, lack of coordination, and weakness, to name a few. Because the variety of symptoms is so vast, it can be challenging to diagnose this condition.
A diagnosis program typically includes a review of your medical history, a physical and neurological exam, blood work, and diagnostic testing.
- Medical History. Your doctor will review your medical history and ask questions regarding your symptoms, severity of pain, and what helps relieve the pain. Other factors may include your work environment, anything that triggers the onset of pain, social habits, exposure to toxins, alcohol and tobacco use, and family history of neurological diseases.
- Physical & Neurological Exam. Your doctor will perform a physical exam to look for any diseases that cause nerve damage, such as diabetes or celiac disease. A neurological exam will determine the cause of a neurological disorder and the severity of nerve damage.
- Blood Work. Blood tests are able to test for vitamin deficiencies, organ dysfunction, infections, and any abnormal bodily system activities. These tests can assist the doctor in determining diseases or disorders that cause neuropathic diseases.
Other tests that can be used to test for peripheral neuropathic diseases are imaging tests, nerve and skin biopsies, and nerve function tests.
Types of Treatments Available
Your doctor will recommend a treatment type based on the type of nerve damage, symptoms you display, and the area that is affected. With the guidance of a pain management specialist, you may be able to manage your neuropathic pain and reduce medications. As long as the nerve cell has not died, the consistent and definitive treatment allows for a functional recovery over time.
Treating Underlying Causes
By correcting the underlying cause of your neuropathy, it can many times heal itself and the nerves can recover and regrow. Simple lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a nutritious diet, and taking vitamin supplements can improve nerve health. Exercise delivers more blood, oxygen, and nutrients to nerve endings, therefore improving muscle strength and preventing muscular atrophy. Controlling glucose levels has also been shown to reduce neuropathic symptoms and help people with diabetes avoid nerve damage.
If an autoimmune disease or inflammation causes your peripheral neuropathy, symptoms can be controlled by using medications like prednisone. A procedure that involves stripping your blood of immune system cells and antibodies, called plasmapheresis, helps reduce inflammation or subdue immune system activity.
Using Medications
When your peripheral neuropathy is not caused by an underlying disease, medications can be used to minimize symptoms.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers. Medications such as NSAIDs like naproxen, ibuprofen, and aspirin can relieve minor symptoms.
- Topical Treatments. Ointments that contain a substance found in hot peppers has been proven to reduce neuropathic symptoms. Lidocaine patches also provide pain relief, although side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, or numbness.
- Antidepressants. Antidepressants interfere with the chemical processes in your brain that cause pain. Tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline help relieve pain. Drugs like Cymbalta (inhibitor duloxetine) may also ease neuropathic pain. Antidepressants have been known to cause side effects such as nausea, drowsiness, or constipation.
Spinal Cord Stimulation
Spinal cord stimulators (SCS) have been used to treat pain for over 50 years. The implanted device transmits therapeutic electrical signals to provide a therapeutic effect. Neuropathic pain is caused by damaged tissue and nerves. Spinal cord stimulators are surgically placed under the skin. They send mild electrical signals to the spinal cord and nerve fibers. These signals mask pain signals before they can reach the brain.
Therapies to Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
Therapy that helps ease the pain of peripheral neuropathy include:
- Physical Therapy. Muscle weakness and physical disabilities caused by peripheral neuropathic diseases can be reversed under the supervision of a physical therapist and a specialized exercise program. Braces, canes, and walkers may be used to aid treatments.
- TENS. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation delivers a gentle electrical current at various frequencies. Electrodes are placed on the skin over the affected area.
- Plasma exchange. Plasma therapy means your blood is removed, processed to remove antibodies, and returned to your body. This helps suppress the immune system activity that causes inflammation.
Surgery for Peripheral Neuropathy
For some types of neuropathies, surgery is the recommended treatment option. Pinched nerves or conditions that compress nerve roots are generally treated with surgery to free the damaged nerve and allow for proper healing. Mononeuropathy is caused by compression or infections and often requires surgery to release pressure on the nerve.
Polyneuropathies such as diabetic neuropathy is not treated with surgery. If you suffer from polyneuropathy, surgery could potentially make your pain worse. Surgery that involves cutting or injuring the nerve can cause damage to the central nervous system. This has been known to cause phantom pain.
With the evolution of technology, less damaging procedures such as electrical stimulation have replaced surgery to treat peripheral neuropathy. To make an appointment or learn more about peripheral neuropathy, fill out the form below.
Degenerative adult scoliosis, also known as adult-onset scoliosis, is when the facet joints and intervertebral discs deteriorate and lead to a curve in the spine. This side-to-side curve occurs over time as a person gets older. It commonly begins after age 40, and is more frequently seen in patients who suffer from osteoporosis. Osteoporosis causes the bones to lose bone density, quickening the deterioration rate. The spine can begin to “lose shape,” and a scoliotic curve can develop.
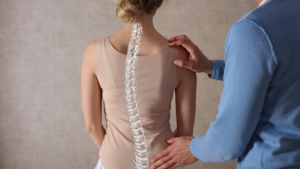
What is Degenerative Scoliosis?
Causes of Degenerative Scoliosis
Age is the leading cause of degenerative scoliosis. Over time, facet joints and discs can deteriorate over time, causing the spine to weaken and lose shape. The joints and discs are what make your back flexible. The joints enable bending and twisting. The discs act as shock absorbers.
Degenerative changes are all part of getting older; however, there are other conditions that cause degeneration at high rates:
- Arthritis: Weak joints and irregular vertebral alignment caused by pressure on the spine.
- Osteoporosis: Loss of bone density weakens the bones and their stability.
- Spine Surgery: Recovery and time after a spinal surgery can cause spine deformities.
Aging joints, combined with any of the factors above, can cause significant deformity. Mild-to-moderate deformity is common in older people but can appear in people as young as their 40s. Studies show that approximately 60% of people over the age of 60 have mild degenerative scoliosis.
Treatments
Degenerative adult scoliosis can cause pressure on the nerves and along the spinal cord. This leads to weakness, numbness, and pain in your lower extremities. In extreme cases, the pain and weakness can make walking difficult.
Unlike scoliosis in adolescents, treatments for spine deformity in adults is determined by the severity of the symptoms, not the severity of the curve of the spine. Treatments tend to focus on managing the pain and reducing symptoms as opposed to correcting the curve.
For mild-to-moderate cases, treatment usually consists of pain management and physical therapy (PT). PT is used to increase mobility of the spine. Low-impact exercises may be used to help restore strength of the spine, with hopes of decreasing the symptoms and rate of deterioration. Over-the-counter medications can be used to manage and reduce pain. NSAIDs help minimize pain caused by inflamed joints or arthritis. Medications are not used to heal the spine, but to reduce pain caused by the curvature of the spine. Reducing pain can allow a patient to resume normal daily activities while they work to regain strength and flexibility.
Other ways to treat degenerative adult scoliosis include:
- Weight Loss: Losing weight helps decrease the pressure placed on facet joints
- Nutrition: Eating foods that help reduce anti-inflammatory properties – such as tumeric and ginger – help reduce the pain. Drinking water is important
- Bracing: A brace is used to restrict motion to relieve pain during daily activities and perhaps during physical therapy. Braces can also be used to decrease stress on the facet joints.
If the symptoms and curvature of the spine is severe, your doctor may recommend surgical options. Surgery is used when the patient’s pain is so severe that is become debilitating or when there is nerve damage from the spine curving. Nerve damage can result in the loss of normal bodily functions such as walking or bladder control.
To learn more about degenerative adult scoliosis, contact the team of experts at Progressive Pain Management. Fill out the form below to get in touch today.
When you live with pain, the change in seasons isn’t always a welcomed change. Warmer weather and humid days may have your running for air conditioning. The expectations of summer typically include spending time outside, having cookouts, and even going on vacation – all things that can increase the symptoms of chronic pain.
Pain can take away from the joys of summer. It can mean getting out of bed in the morning is difficult, and instead of playing with the family, maybe you are just sitting inside and not being active.
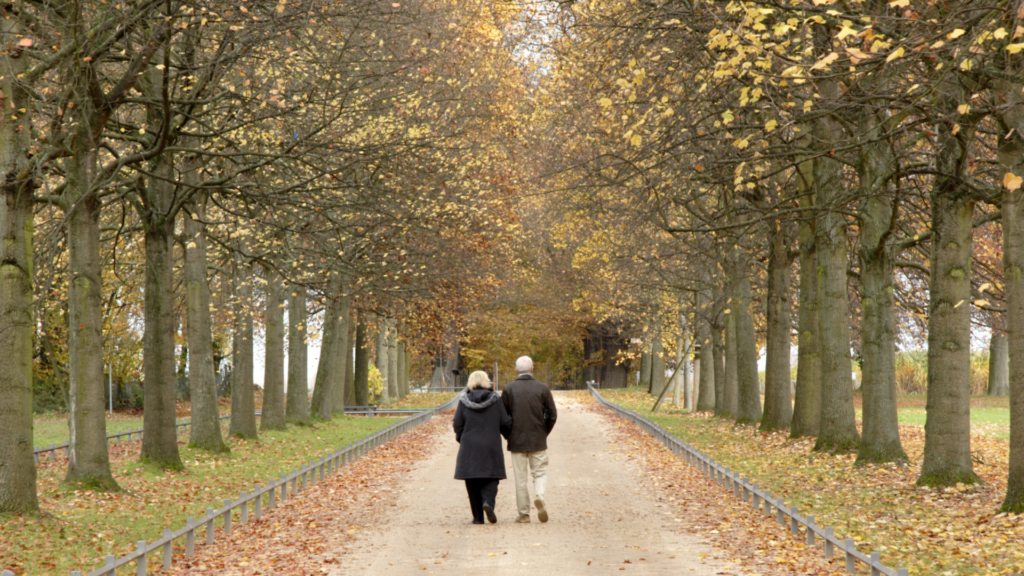

Walking to Reduce Pain
However, although the heat can sometimes worsen your pain, various activities help relieve pain and strengthen your joints. By incorporating these activities into your daily life, you can get outside and enjoy the summer months.
Activities to Combat Reduce Pain
-
Yoga
Yoga has known health benefits, and has become the standard to promote relaxation and overall wellness. There are specific yoga poses that help reduce back pain, joint pain, and can help increase your range of motion.
Doing yoga in hot weather can help improve flexibility and even increases its effectiveness. Being in the heat has the same effect as hot yoga, which detoxifies the body, boosts your mood, and promotes mindfulness. Head to a park or the beach to practice some yoga this summer and find relief from your pain.
-
Indoor Swimming
Swimming is a fun way to relax and reduce pain. Swimming, water aerobics, and low-impact cardio exercises in the water are effective and safe ways to practice strength training, build muscle, and help reduce pain associated with sports injuries, arthritis, and sciatica. The water creates a natural resistance while relieving the pressure on your joints. Being in the water also naturally lowers your blood pressure.
-
Biking
Going for a bike ride on a smooth terrain is a great low-impact cardio exercise that strengthens muscles and can help relieve pain. The way you sit on a bike is helpful to those with spinal stenosis. Getting your blood flowing with some light exercise helps release endorphins, which act as your body’s natural pain killer, and can help improve your mood.
-
Lounging in a Hammock
What better way to enjoy the fall temperatures than with some rest in the shade. Laying in a hammock is a great way to enjoy the warmer weather while simultaneously getting rest and taking some pressure off your sore joints. Hammocks allow your body to rest in a very natural position, with your head slightly elevated. Hammocks also prevent you from rolling in your sleep, which can result in uncomfortable or potentially painful positions.
5. Hiking
Going for a walk or low-impact hike is a light aerobic exercise that improves your stability, burns calories, and corrects posture for multiple muscle groups. Make sure you are keeping your spine straight and allowing your core muscles to do the majority of the work.
Getting your blood flowing and incorporating some low-impact cardio exercises into your summer schedule is important to your overall health. Being outside and getting fresh air and sunlight can do wonders for your mood and help other aspects of your health – not just help reduce pain.
Fill out the form below to get in touch with the team at Progressive Pain.

